Indiana College scientists with experience in optometry and synthetic intelligence are among the many first three teams of researchers to obtain help from a brand new program from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being supporting the rising discipline of “oculomics,” which makes use of the attention as a lens on ailments that have an effect on the entire physique.
Stephen A. Burns, a professor on the IU Faculty of Optometry, has been named a principal investigator on a three-year, $4.8 million award from the NIH Enterprise Program Oculomics Initiative. Among the many co-investigators on the award is Eleftherios Garyfallidis, an affiliate professor of clever techniques engineering on the IU Luddy Faculty of Informatics, Computing and Engineering.
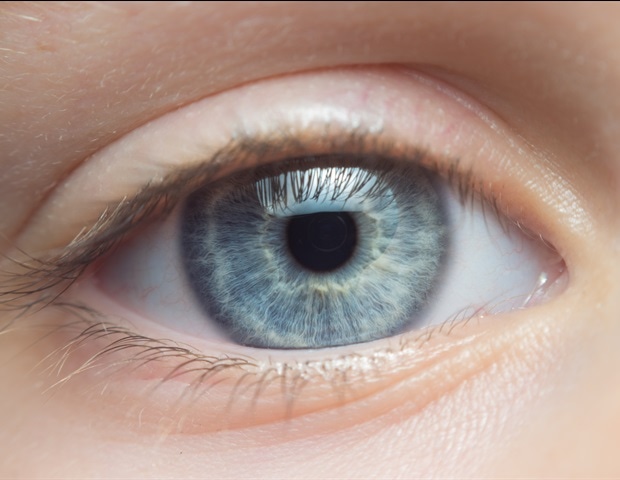
The venture will help the event of next-generation ophthalmoscopes -; devices to watch the inside of the attention -; that may spot the early warning indicators of circumstances akin to diabetes, coronary heart illness, kidney illness, sickle cell anemia and Alzheimer’s illness with a easy eye scan.
“This analysis is about utilizing the attention as a window on well being,” Burns stated, noting that the retina is the one instantly observable a part of the central nervous system. “We wish to give well being care suppliers the clearest view they will hope to get into the physique, non-invasively.”
Extra researchers on the venture embody co-principal investigator Amani Fawzi of Northwestern College and co-investigators Alfredo Dubra of Stanford College and Toco Y. P. Chui of the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
Burns’ analysis on utilizing the attention to detect illness goes again to the early 2000s, when he and colleagues on the IU Faculty of Optometry pioneered making use of adaptive optics scanning laser techniques to the commentary of the human eye. The sphere was initially developed by astronomers to get rid of the “twinkle” of stars -; or distortions trigger by the Earth’s ambiance -; in telescopes. The optics of the attention produce related mild distortions.
Utilizing the know-how developed on the college, the ophthalmoscope in Burns’ lab can observe the again of the human eye on the decision of two microns -; a scale sufficiently small to point out the real-time motion of purple blood cells inside the attention’s arteries and veins. (A single purple blood cell is roughly eight microns in width.) Burns has used the know-how to establish biomarkers for diabetes and hypertension within the partitions of the attention’s blood vessels.
Mission researchers from Northwestern and Mount Sinai have used related know-how to watch the cells each inside and outside these blood vessels, together with recognizing the crescent-shaped purple blood cells present in sickle cell anemia. The Stanford researchers have used adaptive optics to enhance commentary of the attention’s photoreceptors.
With help from the NIH, the analysis groups will combine their particular person tasks right into a singular system, in addition to apply state-of-the-art machine studying and AI. Moreover, they’ll discover the know-how’s potential to identify the early indicators of coronary heart illness and Alzheimer’s illness.
There’s rising proof of a robust retinal vascular element to Alzheimer’s illness. You may at the moment see the indicators with PET scans, which require massive, multimillion-dollar devices. If we will see the identical indicators with a watch scan, it is so much much less invasive and so much less expensive.”
Stephen A. Burns, Professor, IU Faculty of Optometry
Garyfallidis’ position is growing and making use of the machine studying and AI strategies for deciphering the units’ outcomes. This might cut back prognosis time from days to minutes by eliminating the necessity for a human to investigate the imagery.
Within the first 12 months of the venture, the labs will align their devices to the identical stage of sensitivity, stated Burns, whose lab will combine its know-how with Northwestern’s instrument. Stanford will give attention to related technological integrations with the instrument at New York Eye and Ear.
Subsequent, the work will shift towards information validation to verify that the brand new devices’ readings align with earlier variations of the know-how. The researcher may even examine the brand new AI system’s interpretation of scans in opposition to the conclusions of human analysts to verify accuracy.
The ultimate 12 months of the venture will contain testing the system on medical volunteers. A lot of IU’s information will come from people recruited by the Atwater Eye Care Middle.
“As much as 80 % of the inhabitants over the age of 60 has at the very least one well being situation that could be detectable within the eye with our know-how,” Burns stated.
He stated the NIH chosen the venture because of potential for prime impression. Enterprise Fund initiatives emphasize “transient, modest investments that may be carried out rapidly, with a robust potential to speed up science.”
“Our problem now’s selectivity and specificity,” Burns stated. “We have to present that we will detect the variations between circumstances, to rapidly and precisely interpret the indicators of the assorted ailments we’re specializing in.”
The aim is to advance the know-how till it is able to make the leap from the lab to “wherever you get your annual eye examination,” he stated.