Why are energy eaten within the morning much less fattening than energy eaten within the night?
One motive energy consumed within the morning are much less fattening than these eaten within the night is that extra energy are burned off within the morning attributable to diet-induced thermogenesis. That’s the quantity of vitality the physique takes to digest and course of a meal, given off partly as waste warmth. If persons are given the identical meal within the morning, afternoon, or night time, their physique makes use of up about 25 p.c extra energy to course of it within the afternoon than at night time and about 50 p.c extra energy to digest it within the morning, as you possibly can see under and at 0:36 in my video Eat Extra Energy within the Morning Than the Night. That leaves fewer web energy within the morning to be saved as fats.
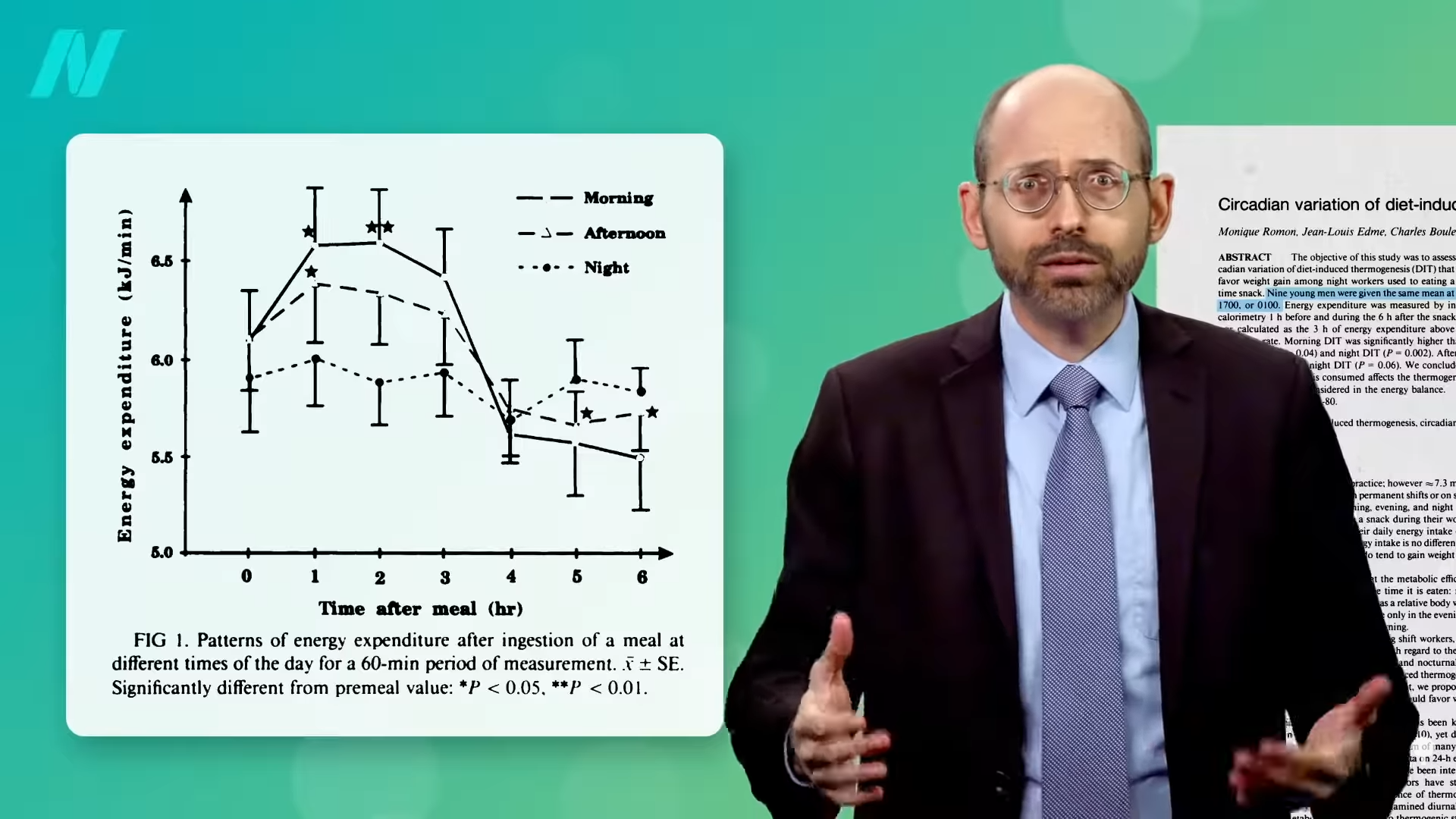
Let’s put some precise numbers to it. A bunch of Italian researchers randomized 20 individuals to eat the identical standardized meal at both 8:00 am or 8:00 pm and had them return per week later to do the other. So, every particular person had an opportunity to eat the identical meal for breakfast and dinner. After each meal, the research individuals had been positioned in a “calorimeter” contraption to exactly measure what number of energy they had been burning over the following three hours. As you possibly can see under and at 1:18 in my video, the researchers calculated that the meal given within the morning took about 300 energy to digest, whereas the identical meal given at night time solely used up about 200 energy to course of. The meal was about 1,200 energy, however, when eaten within the morning, it ended up solely offering about 900 energy in comparison with extra like 1,000 energy at night time. Identical meal, similar meals, similar quantity of meals, however successfully 100 fewer energy when consumed within the morning fairly than at night time. So, a calorie is not only a calorie. It depends upon after we eat it.
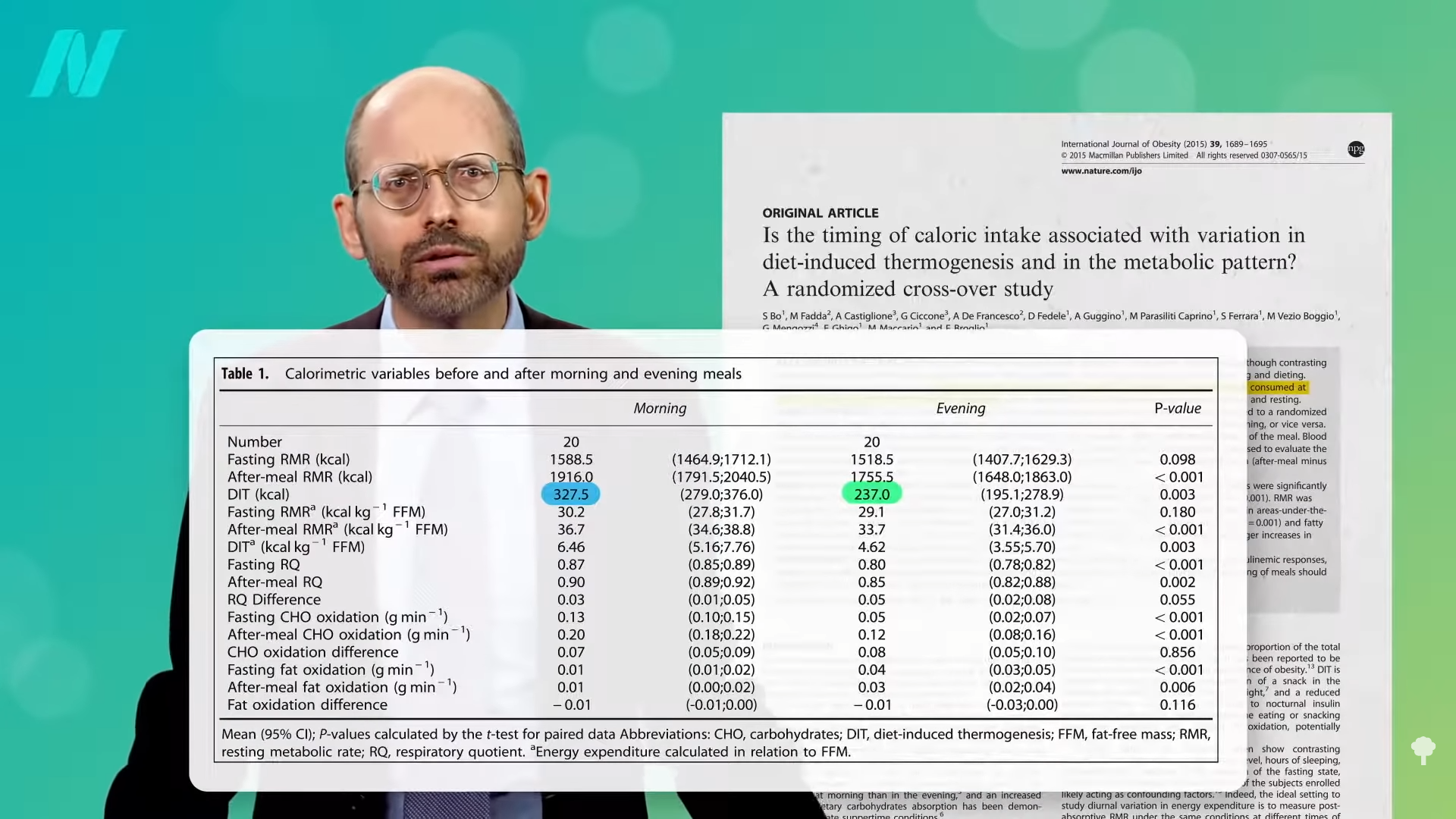
However why can we burn extra energy when consuming a morning meal? Is it behavioral or organic? In case you began working the graveyard shift, sleeping throughout the day and dealing all night time, which meal would web you fewer energy? Wouldn’t it be the “breakfast” you had at night time earlier than you went to work or the “dinner” you had within the morning earlier than you went to mattress? In different phrases, is it one thing about consuming earlier than you fall asleep that causes your physique to carry onto extra energy, or is it constructed into our circadian rhythm, the place we retailer extra energy at night time no matter what we’re doing? You don’t know till you place it to the check.
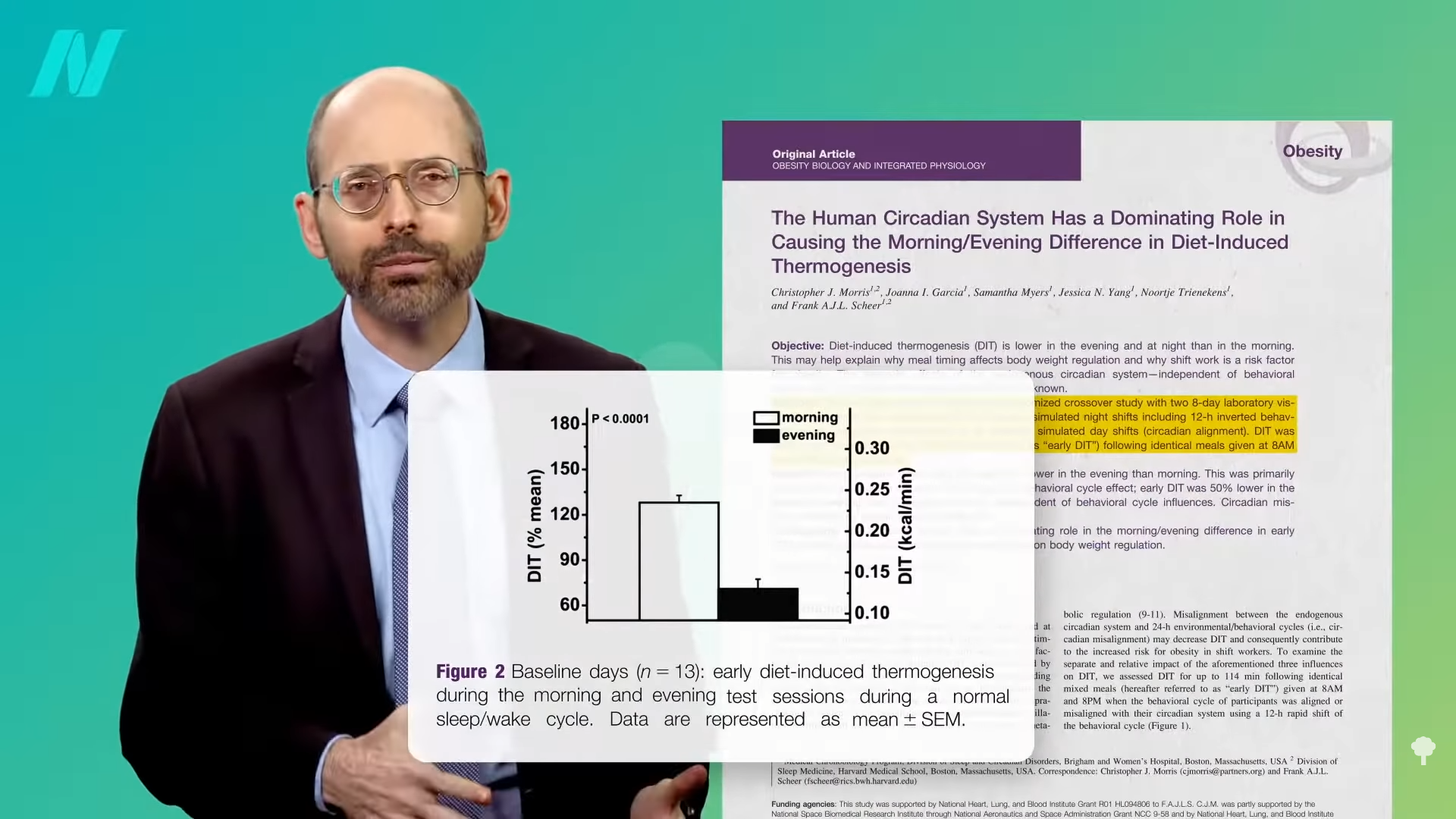
Harvard researchers randomized individuals to an identical meals at 8:00 am versus 8:00 pm whereas underneath simulated night time shifts or day shifts. No matter exercise degree or sleeping cycle, the variety of energy that had been burned processing the morning meals was 50 p.c larger than within the night, as you possibly can see within the graph under and at 2:45 in my video. So, the distinction is defined by chronobiology: It’s simply a part of our circadian rhythm to burn extra meal energy within the morning. However, why? What precisely is occurring?
How does it make sense for our physique to waste energy within the morning when we’ve got the entire day forward of us?
Our physique isn’t a lot losing energy as investing them. After we eat within the morning, our physique bulks up our muscle groups with glycogen, which is the first vitality reserve our physique makes use of to gas our muscle groups, however this takes vitality. Within the night, our physique expects to be sleeping for a lot of the following 12 hours, so fairly than storing blood sugar as additional glycogen in our muscle groups, it preferentially makes use of it as an vitality supply, which can find yourself which means we burn much less of our backup gas (physique fats). Within the morning, nevertheless, our physique expects to be working round all day, so as an alternative of simply burning off breakfast, our physique continues to dip into its fats shops whereas we use breakfast energy to stuff our muscle groups filled with the vitality reserves we have to transfer round over the day. That’s the place the “inefficiency” might come from. The explanation it prices extra energy to course of a morning meal is that, as an alternative of simply burning glucose (blood sugar) instantly, our physique makes use of up vitality to string glucose molecules collectively into chains of glycogen in our muscle groups, that are then simply going to be damaged again down into glucose later within the day. That additional meeting/disassembly step takes vitality—vitality that our physique takes out from the meal, leaving us with fewer energy.
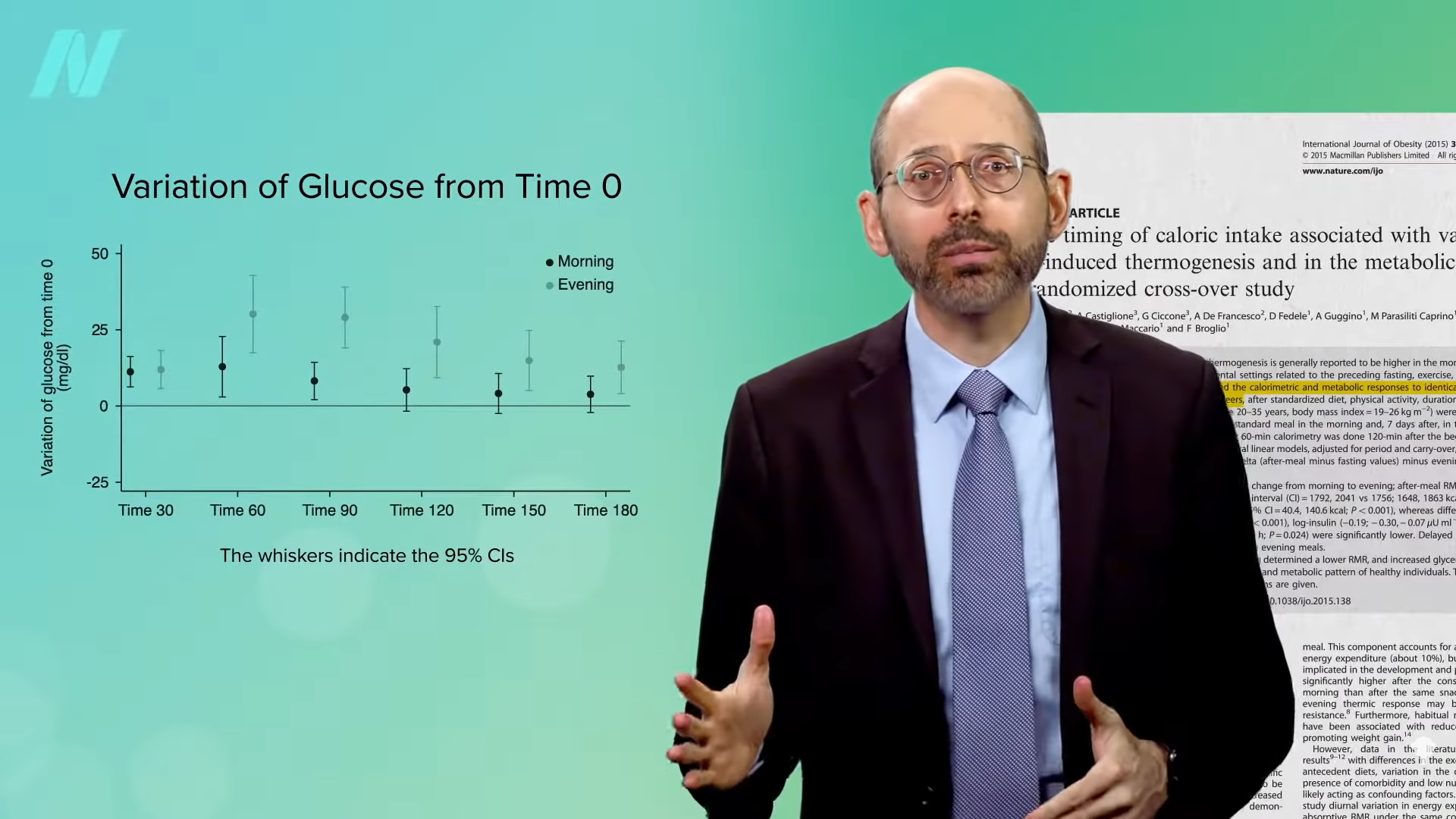
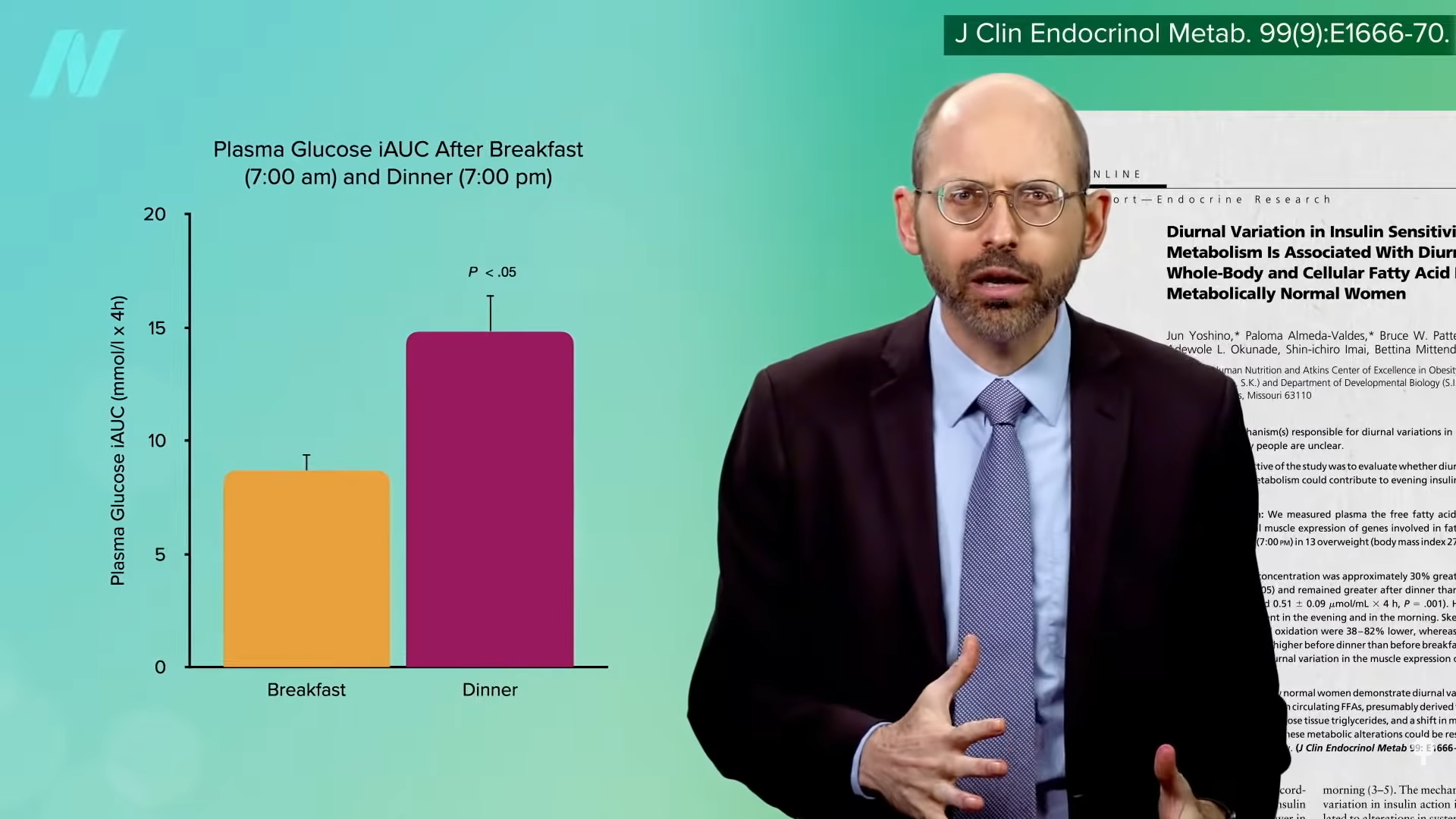
So, within the morning, our muscle groups are particularly delicate to insulin, quickly pulling blood sugar out of our bloodstream to construct up glycogen reserves. At night time, although, our muscle groups develop into comparatively insulin-resistant and resist the sign to soak up additional blood sugar. So, does that imply you get the next blood sugar and insulin spike within the night in comparison with consuming the identical meal within the morning? Sure. As you possibly can see within the graph under and at 5:02 in my video, in that 100-calorie-difference research, for instance, blood sugars rose twice as excessive after the 8:00 pm meal in comparison with the identical meal eaten within the morning.
So, shifting the majority of our caloric consumption in the direction of the morning would seem to have a twin profit—extra weight reduction, and higher blood sugar management, as proven within the graph under and at 5:12 in my video.
In case you thought twin advantages sounded good, keep tuned for triple advantages! I dive deeper into circadian rhythms. See associated posts under.
My previous few movies (see under) give attention to why science factors to loading your energy in the direction of the start of the day.